What is Google Analytics 4: A User's Guide to the New Analytics System
•September 15, 2022 • 10 minutes to readFor the past 10 years, Universal Analytics was used as the default for all websites using Google Analytics to track goals, events, and overall traffic. However, as of October 2020, the new GA4 was made available as an option - soon to be the only choice as of July 1, 2023. This guide will explain:
- how GA4 differs from the UA version
- how to switch your existing accounts to it
- how to use it in your organization
What Distinguishes Google Analytics 4 From Earlier Versions
Google Analytics 4 is positioned as a new, smarter version of Google's current analytics solution.
The primary distinction between Google Analytics 4 and Universal Analytics is a different data collecting method. Data in Universal Analytics is gathered based on page visits, but data in Google Analytics 4 is collected based on events using an event-driven data model.
Advantages of Google Analytics 4
Switching your analytics system can seem daunting, but there are distinct advantages to using GA4, including:
- Tracking across several platforms - Google Analytics 4 gathers and aggregates data from websites and mobile apps into a single report. As a result, you no longer need to use separate analytics systems for websites and apps.
- Improved stats - Unlike Universal Analytics, which only gathered data on page visits, Google Analytics 4 displays scroll depth, outbound clicks, site searches, video interactions, and other metrics.
- Effective analytics tools - As a center for analysis, Google Analytics 4 enables you to create your own reports and analyze them using any measure, including visualizing user journeys and cohorts, comparing groups, creating your own conversion funnels, and more. Such changes were previously accessible exclusively to Google Analytics 360 members, but they are now open to everyone.
- In-depth examination of user activity - In Google Analytics 4, there is no such thing as a "bounce rate." Instead, GA4 takes a different approach to tracking user activity, enabling you to discover, for example, which items people most often purchase, what content is consumed by visitors of all ages, and which country’s users are more likely to view videos.
- Predictive purchasing - Based on user behavior data, individuals are divided into those who are likely to make a purchase within 7 days and those who are likely to depart with nothing.
Universal Analytics vs. Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 differs significantly from Universal Analytics in terms of both interface and capabilities. We can see the following improvements:
- More options for making your own reports
- Focus is on user behavior rather than sessions
- Effective audience research tools
For those transitioning from Universal Analytics, you’ll need to navigate the challenges of transferring reports, understanding new metrics, and making sense of the new data-gathering infrastructure.
GA4 has received several upgrades, the most notable of which enables you to efficiently evaluate cross-platform interactions. For example, you will be able to follow a user who visited your site today and viewed items, then installed an app on their mobile phone the next day and completed a purchase.
In addition, data from different site analytics platforms can now be mixed in GA4. Previously, Firebase Analytics was utilized for apps, whilst Google Analytics was largely used for websites. This meant you had to manually examine data from several sources, which took a significant amount of time and effort.
What Else Does Google Analytics 4 Offer?
Let's look at some of the best aspects of GA4 that you can absolutely put to use:
- Center for Analysis You may utilize the Analysis Center to produce reports and analyze data from metrics that interest you, such as studying the behavior of certain users. The service also includes pre-made templates (free form, funnel exploration, cohort exploration, path exploration, segment overlap, user explore, etc) that will make your life much easier, in addition to a customizable event accounting system.
- Google BigQuery Data Management GA4 users will be able to access raw data in order to integrate it with other sources or execute SQL queries. You can store data and/or send it to your warehouse, enrich your data with CRM/marketing/contextual data, visualize data with other tools and perform advanced analytics on it including the ability to use it as an input for machine learning models.
- New Engagement Indicators / Improved Metrics If you track the behavior of visitors who explore and engage with your site or app, you'll want to know which sections are read the most, which videos are watched, which files are actively downloaded, etc. To do this, GA4 employs an upgraded method of tracking user interaction. Page hits, event hits, e-commerce hits, and social interaction hits are all Universal Analytics hit kinds. Google Analytics 4 data, on the other hand, is event-based, with the notion that any interaction may be logged as an event. As a result, Universal Analytics property hit types correspond to Google Analytics 4 property events, but with a wider view of intent, and therefore more meaningful data sets.
- Purchase Propensity The tool enables you to create user groups based on their chance of placing an order or leaving the site or app within the following seven days. GA4 does this by analyzing its network activity and making predictions.
Migration Challenges Presented by GA4
When migrating to GA4, you may bump into some unexpected challenges as a result of the new Event + Parameter paradigm and service redesign, namely:
- Some regular reports that marketers use are altered or absent from the service.
- The process of adding tags has evolved dramatically.
- Some well-known measures, such as bounce rate, have been eliminated.
- There are new metrics to consider.
- Report migration takes extra time.
- There is no automated data transfer from UA to GA4.
Nonetheless, this is not an excuse to pass on a fantastic new product that will provide several advantages to your business in the future.
How to Make the Switch to Google Analytics 4
As you transition, what you consider depends on whether you have an existing UA instance set up, or you are starting from scratch:
- For new users, only Google Analytics 4 is accessible. You do not have the option to install Universal Analytics on your site.
- Existing users are not automatically updated from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4, so they must make the switch
Methods for Migrating to Google Analytics 4
To get started, you may not know the right place to even begin, so here are your first steps:
- Make a brand-new property.
When you create a new property, the key settings from Universal Analytics are duplicated and migrated to GA4. You may alter your parameters–conversions, audiences, events, and linkages to other products (Google Ads Links, Ad manager Links, BigQuery Links, etc)–as necessary. - Connect the existing Universal Analytics property to the new Google Analytics 4. Only property administrators have access to this procedure. The bottom line is to connect the old and new properties before migrating the Google Analytics setups.
GA4 Upgrade: What to do next
- Navigate to the "Admin" area of your Universal Analytics account:
- Select the "Upgrade to GA4" item from the "Property" column:
- You will see two options: build a new property or connect an existing property to a new one.
- To create a new property, click the "Get Started" button next to the item "I need to make a new Google Analytics 4 property."
- Following these steps, the link between the old UA property and the new GA4 property will be established. Click the "View GA4 property" button to go to a different property.
- After moving to Google Analytics 4, a new identification will emerge, which is a nine-digit numerical number after the UA qualifier. In contrast, the Universal Analytics ID (UA) is identified simply with nine digits.
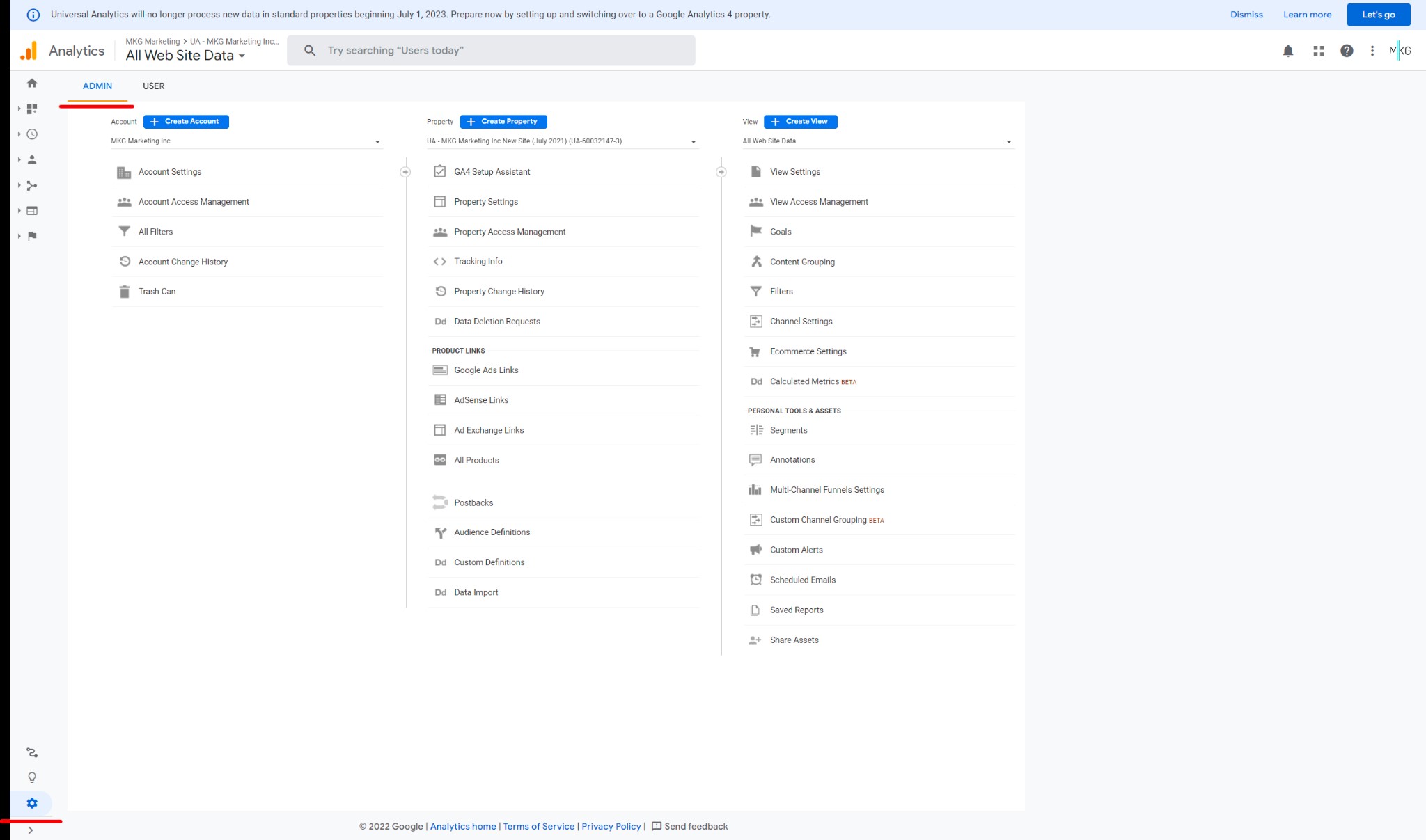
Configuring a property in GA4
If you followed the steps above, a new Google Analytics 4 property has now been created. However, your property will require some fine-tuning to function properly. Let's quickly go through the essential steps.
In the "Admin" area, click "Create a property" to create a property. Then take these additional steps for configuring Google Analytics 4, which are divided into five categories:
- Establishing a property - Give the account a name, choose the time zone, and specify the currency.
- Adding details about the organization we’re tracking - Choose the industry type, the size of the organization, and the reason for employing Universal Analytics.
- Setting up the data flow - Choose a data source for the property from the list: online stream, Android app, or iOS app. Each stream is set up independently if multiple threads are needed. To create a web stream, provide the site URL and the stream name. Set up your mobile app stream through Firebase. Google Analytics requires the Firebase SDK which unlocks most Firebase features and includes Analytics for iOS and Android apps.
- Tagging the website - There are two options: create a new tag or utilize an existing one. Using an existing tag enables flow labeling without modifying the page's code. However, the page must already have the gtag.js tag for this to work.
- Copy the global tag to add a new tag to the page. The global tag must be included within the head tag of each page of the site that needs to be monitored.
- You can also use Google Tag Manager to add the global tag.
- After you've added the tag to the site, you may add additional data streams.
- Creating a link between Google Analytics 4 and Google Ads - Select "Link with Google Ads" in the "Link with other goods" section:. Select the relevant Google Ads account and customize the parameters in the link settings (by default, personalized advertising and the auto-tagging function are enabled).
The majority of the work on establishing the property has been finished. Following that, audiences are set up (an audience is chosen for further segmentation, and remarketing is established), and conversion monitoring and access control are put in place.
Using the Google Analytics 4 Interface
Dashboards are used to show information in Google Analytics 4. The main page displays summary information about users on your site and apps, such as site traffic, the number of new visitors for a specific period, average time spent on the site, nationality, and so on.
Google Analytics 4 Menu Walkthrough
The menu structure has changed significantly from the menu in Universal Analytics. The UA menu was separated into two sections: Special Reports (reports that may be customized individually) and Reports (standard system reports). The menu in Google Analytics 4 is tailored to user analytics; sections are described below.
- The Life Cycle - Displays information regarding visitor activity on the site/application. The amount of new users, user acquisition methods, engagement, and monetization are all shown here.
- The User - There are two reports available here: Demographic Data and Technical Data.
The Demographic Data report enables you to identify generally and geographically:- Overall user count
- Sessions per user
- Average amount of time spent interacting with a property
- Total number of conversions
- Total earnings
The Technological Data report will tell you what device, operating system, and browser the visitor used, as well as how they interacted with the channel. - Occurrences - Offers information about all key events and conversions on the site/app.
Event data is not accessible immediately after the property is created. Tags must be set up before data can be shown. Following that, conversion event reports will be available within 24 hours.
Google Analytics 4 automatically records events, which are the most common user behaviors on your website or app. Here are some instances of events that are automatically registered right out of the box:- ad_click - click on an ad within the app
- ad_impression - ad impression within the app
- page_view - loading a page on the website
By default, the system gathers five parameters for all events (both automated and manually created):- language - user's browser language
- page_location - URL of the page
- page_referrer - URL of the previous page the user visited
- page_title - title of the page
- screen_resolution - resolution of the screen being used
You may construct an event-based conversion in Google Analytics 4. These are the events most significant to your business. Built-in conversion events include the following:- first_open - the first launch of the application after installation
- in_app_purchase - in-app purchase or subscription
- app_store_subscription_convert - registration of a paid subscription after the trial period
- app_store_subscription_renew - renewal of a paid subscription
- purchase - purchase of a product or service The rest of the conversion events need to be set up manually.
- General Overview - This section provides a collection of audience research tools.
You must go to the Analysis Center to examine the audience. You may do your own analysis and research there.
There are ready-made reports in the Template Gallery, such as free form, funnel exploration, cohort exploration, path exploration, segment overlap, user explore, etc - Personalize - You may add a new audience, define user and audience traits for them, and manage access privileges in this area.
Now it’s your turn
This concludes our initial walkthrough. Are you still finding the GA4 migration tough to grasp?
MKG Marketing’s digital marketing analytics experts can assist you with migrating to GA4, setting up the tracking and new reports as well as get you comfortable with monitoring your data on the GA4 project dashboard. Schedule a discovery call today!




